Lipid( Fat& waxes)
Introduction
Lipids are the substances of animal or plant origin and
comprise of fixed oils, fats and waxes. The basic function of oils and fats is
storage of energy, apart of their several uses in medicines and industries. They
are obtained by expression or extraction methods.
Fats and oils
Properties
1 Fixed
oils are thick, yellow colored liquids (In case of fixed oil) & semi solid
(in case of fats, viscous with characteristic odour. They
are non-volatile and cannot be distilled. They
do have food value & they can be converted into soap by heating with alkali
(Saponification). They turn rancid on storage due to free
acidity. Fixed oils and fats are insoluble in water and
ethyl alcohol, but soluble in organic solvents. Fats
and oils are esters of glycerol.
7 Fat:
- Fats are solid or semisolid at 15.50 to 16.50 C while fixed oils are liquid
at this temp.
Lipids chemistry
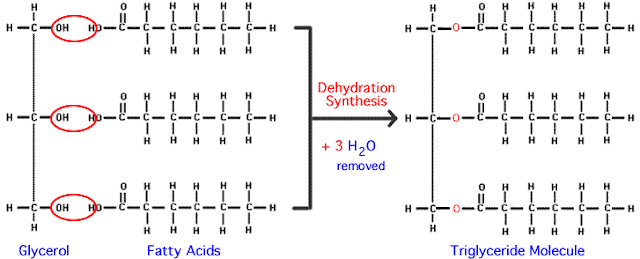
Fats and oils are esters of
glycerol (three carbon trihydric alcohol). The fatty acids of natural fats have
4 to 24 carbon atoms (and in any even number). These fatty acids may be
saturated, monounsaturated, polyunsaturated.
Triglyceride
Lipids extraction
Extraction of fixed oils and fats
1. Vegetable origin– expression
a. cold expression – cold-pressed
oil or virgin oil
b. hot expression– hot pressed oil
2. Animal origin– steam with or without pressure
Waxes
Waxes are esters of fatty acid
along with high molecular weight monohydric alcohols such as cetyl alcohol,
cholesterol, melissyl alcohol.
They are insoluble in water. They
are soluble in organic solvents, solids. They have characteristic waxy luster
they milt on heating. They are unctuous to touch.
e. g.
a) Animal wax- Bees wax, spermaceti.
b) Vegetable wax- Japan wax,
carnauba waxes.
c) Mineral- Hard paraffin ceresin
The difference between fats &
waxes is that, waxes can be saponified only by alcoholic solution of alkali
while fixed oil can be saponified by aqueous as well as alcoholic solution of
alkali.
Analytical parameters for Oils and
Fats
USP specifications to determine
identity, purity, quality of fixed oils(chemical constituents) of fatty acids
1. Acid value (acid number)
2. Saponification value
3. Iodine value
4. Melting point
5. Specific gravity
6. Refractive index



No comments:
Post a Comment